 |
| In the Adventures of Buck Danny placed during the 80s untill today several famous military aircraft are shown. Mostly of these are US Naval Aviation aircraft but several US Air force and foreign modern aircraft are represented as well. |
 |
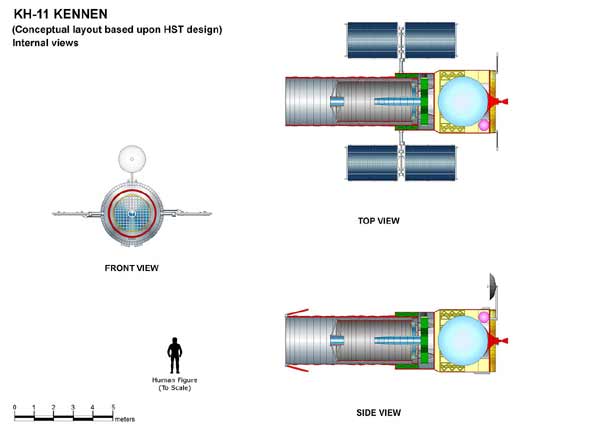
A US National Security Agency reconnaissance satellite KH-11 Kennan is well represented by Bergese in the story LES OISEAUX NOIRS |
 |
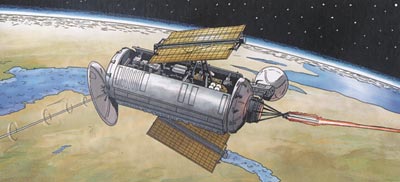
Anoter similar reconnaissance satellite launched from Vandenberg AFB is also represented by Bergese in the same story LES OISEAUX NOIRS |
The KH-11 KENNAN, renamed CRYSTAL in 1982 and according to leaked NRO budget documentation currently going by the codename of Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL (EEC) (but also referenced by the codenames 1010, and "Key Hole"), is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and create a real-time optical observation capability.
Later KH-11 satellites have been referred to by outside observers as KH-11B or KH-12, and by the names "Advanced KENNAN", "Improved Crystal" and "Ikon". Official budget documents refer to the latest generation of Electro-Optical satellites as Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System. The Key Hole series was officially discontinued in favor of a random numbering scheme after repeated public references to KH-7 Gambit, KH-8 Gambit-3, KH-9 Hexagon, and KH-11 satellites. KH-11 satellites are believed to have been the source of some imagery of the Soviet Union and China made public in 1997, as well as images of Sudan and Afghanistan made public in 1998 that were related to the response to the 1998 U.S. embassy bombings.
|
 |
|
US Laser Killer Satellite |
 |
A fantasy Killer satellite armed with a Laser cannon is represented by Le Bras in the second episode of the story LES OISEAUX NOIRS |
Space weapons are weapons used in space warfare. They include weapons that can attack space systems in orbit (i.e. anti-satellite weapons), attack targets on the earth from space or disable missiles travelling through space. In the course of the militarisation of space, such weapons were developed mainly by the contesting superpowers during the Cold War, and some remain under development today. Space weapons are also a central theme in military science fiction and sci-fi video games.
On March 23, 1983, President Ronald Reagan proposed the Strategic Defense Initiative, a research program with a goal of developing a defensive system which would destroy enemy ICBMs. The defensive system was nicknamed Star Wars, after the movie, by its detractors. Some concepts of the system included Brilliant Pebbles, which were Kinetic Kill Vehicles, essentially small rockets launched from satellites toward their targets (a warhead, warhead bus, or even an upper stage of an ICBM). Other aspects included satellites in orbit carrying powerful lasers or particle beams. When a missile launch was detected, the satellite would fire at the missile (or warheads) and destroy it. Although no real hardware was ever manufactured for deployment, the military did test the use of lasers mounted on Boeing 747s to destroy missiles in the 2000s, however these were discontinued due to practical limitations of keeping a constant fleet airborne near potential launch sites due to the lasers range limitations keeping a small number from being sufficient. The tests took place at Edwards Air Force Base
|
 |
|
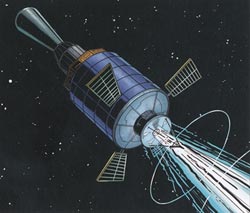
Istrebitel Sputnikov (Satellite Fighter) |
 |
A possible Russian "Satellite Fighter" is represented by Bergese in the first episode of the story LES OISEAUX NOIRS |
 |
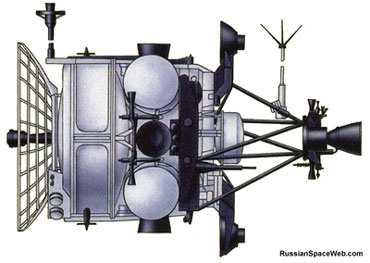
The same Russian "Satellite Fighter" is represented by Le Bras in the second episode of the story LES OISEAUX NOIRS "OPERATION CHECKMATE" |
Istrebitel Sputnik, or IS (Russian: Satellite Fighter, after the meaning "Fighter aircraft" for the Russian word istrebitel), was a Soviet anti-satellite weapons programme which led to the deployment of the IS-A or I2P system during the 1970s and 1980s. IS satellites were originally intended to launch on UR-200 rockets, but following the cancellation of the UR-200, the Polyot, Tsyklon-2A and Tsyklon-2 rockets were used instead.
The first test flights of the IS spacecraft used the I1P configuration, and served to demonstrate the propulsion and control systems of the spacecraft. Both were launched by Polyot rockets, and were designated Polyot 1 and Polyot 2. They were launched on 1 November 1963 and 12 April 1964 respectively. Following this, IS-A or I2P interceptors and IS-P or I2M targets were launched. Only four IS-P targets were launched before the type was replaced by the cheaper DS-P1-M satellite, launched as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. Later IS-A tests intercepted DS-P1-M satellites, or the Lira satellites that succeeded them.
|
 |

| A Russian strategic bomber Tu-160 "Blackjack" is represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
The Tupolev Tu-160 Beliy Lebed (or White Swan, NATO reporting name: Blackjack) is a supersonic, variable-sweep wing heavy strategic bomber designed by the Tupolev Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. Although several civil and military transport aircraft are larger in overall dimensions, the Tu-160 is the world's largest combat aircraft to enter service, largest supersonic aircraft, and largest variable-sweep aircraft ever built.
Entering service in 1987, the Tu-160 was the last strategic bomber designed for the Soviet Union. The Long Range Aviation branch of the Russian Air Force has 16 aircraft with fewer in active use. The Tu-160 active fleet has been undergoing upgrades to electronics systems since the early 2000s. The Tu-160M modernisation programme has begun with the first new updated aircraft delivered in December 2014.
|
 |

| A Sukhoi Su-27 of the Russian Air Force is shown by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
Two SU-27 are also used by Jerry Tumbler and Slim Holden in the story COBRA NOIR. |

|

| A Sukhoi Su-27 belong to an international criminal organization is shown in the story TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE |

| The Sukhoi Su-27 (NATO reporting name: Flanker) is a twin-engine supermaneuverable fighter aircraft designed by Sukhoi. It was intended as a direct competitor for the large United States fourth-generation fighters such as the Grumman F-14 Tomcat and F-15 Eagle, with 3,530-kilometre (1,910 nmi) range, heavy aircraft ordnance, sophisticated avionics and high maneuverability. The Su-27 was designed for air superiority missions, and subsequent variants are able to perform almost all aerial warfare operations. Complementing the smaller MiG-29, the Su-27 has its closest US counterpart in the F-15 Eagle.
The Su-27 entered service with the Soviet Air Forces in 1985. The primary role was long range air defence against American SAC B-1B and B-52G/H bombers, protecting the Soviet coast from aircraft carriers and flying long range fighter escort for Soviet heavy bombers such as the Tu-95 "Bear", Tu-22M "Backfire" and Tu-160 "Blackjack".
There are several related developments of the Su-27 design. The Su-30 is a two-seat, dual-role fighter for all-weather, air-to-air and air-to-surface deep interdiction missions. The Su-33 'Flanker-D' is a naval fleet defense interceptor for use on aircraft carriers. Further versions include the side-by-side two-seat Su-34 'Fullback' strike/fighter-bomber variant, and the Su-35 'Flanker-E' improved air superiority and multi-role fighter. The Shenyang J-11 is a Chinese licence-built version of the Su-27.
|

| The two seat version of the SU-27 identified as Sukhoi Su-30 of the Russian Navy is shown by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE In reality the Russian Navy do not use the SU-30 being only the SU-33 actually used by the Russian Navy. |
Another SU-30 is used by Buck Danny as well represented by Winis in the story COBRA NOIR. |

|

| The Sukhoi Su-30 (NATO reporting name: Flanker-C) is a twin-engine, two-seat supermaneuverable fighter aircraft developed by Russia's Sukhoi Aviation Corporation. It is a multirole fighter for all-weather, air-to-air and air-to-surface deep interdiction missions.
The Su-30 started out as an internal development project in the Sukhoi Su-27 family by Sukhoi. The design plan was revamped and the name was made official by the Russian Defense Ministry in 1996. Of the Flanker family, only the Su-27, Su-30, Su-34 and Su-35 have been ordered into serial production by the Defense Ministry. All the others, such as Su-37, were prototypes. The Su-30 has two distinct version branches, manufactured by competing organisations: KnAAPO and the Irkut Corporation, both of which come under the Sukhoi group's umbrella.
KnAAPO manufactures the Su-30MKK and the Su-30MK2, which were designed for and sold to China, and later Indonesia, Venezuela and Vietnam. Due to KnAAPO's involvement from the early stages of developing Su-35, these are basically a two-seat version of the mid-1990s Su-35. The Chinese chose an older but lighter radar so the canards could be omitted in return for increased payload. It is a fighter with both air supremacy and attack capabilities, generally similar to the U.S. F-15E.
Irkut traditionally served the Soviet Air Defense and, in the early years of Flanker development, was given the responsibility of manufacturing the Su-27UB, the two-seat trainer version. When India showed interests in the Su-30, Irkut offered the multirole Su-30MKI, which originated as the Su-27UB modified with avionics appropriate for fighters. Along with its ground-attack capabilities, the series adds features for the air-superiority role, such as canards, thrust-vectoring, and a long-range phased-array radar. Its derivatives include the Su-30MKM, MKA and MKV for Malaysia, Algeria and Venezuela, respectively. The Russian Air force operates several Su-30s and has ordered the Su-30SM version.
|

| Some SU-33 on board of the Russian Aircraft Carrier Admiral Kusnetzov are shown by Begese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
Another SU-33 is used by Slim Holden as well represented by Winis in the story COBRA NOIR. |

|

| The Sukhoi Su-33 (NATO reporting name: Flanker-D) is an all-weather carrier-based twin-engine air superiority fighter designed by Sukhoi and manufactured by Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association. It is a derivative of the Su-27 "Flanker" and was initially known as the Su-27K. First used in operations in 1995 aboard the carrier Admiral Kuznetsov,[N 1] the fighter officially entered service in August 1998, by which time the designation "Su-33" was used. Following the break-up of the Soviet Union and the subsequent downsizing of the Russian Navy, only 24 aircraft were produced. Attempted sales to China and India fell through.
Compared with the Su-27, the Su-33 has a strengthened undercarriage and structure, folding wings and stabilators, all for carrier operations. The wings are larger than on land-based aircraft for increased lift. The Su-33 has upgraded engines and a twin nose wheel, and is air refuelable. In 2009, the Russian Navy ordered the MiG-29K as a replacement for the Su-33.
|

| The two seat version of the SU-27 identified as Sukhoi Su-30 of the Russian Navy is shown by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE In reality the Russian Navy do not use the SU-30 being only the SU-33 and the two seat side by side SU-34 actually used by the Russian Navy. |
The Sukhoi Su-34 (NATO reporting name: Fullback)[16] is a Russian twin-engined, twin-seat strike fighter. It is intended to replace the Sukhoi Su-24.
Based on the Sukhoi Su-27 'Flanker', the two-seat Su-34 is designed primarily for tactical deployment against ground and naval targets (tactical bombing/attack/interdiction roles, including against small and mobile targets) on solo and group missions in daytime and at night, under favourable and adverse weather conditions and in a hostile environment with counter-fire and EW counter-measures deployed, as well as for aerial reconnaissance.
|

|

| A Russian Aerial Refuelling Tanker Il-78 is well represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
The Ilyushin Il-78 (NATO reporting name Midas) is a four-engined aerial refuelling tanker based on the Il-76.The Il-76 tanker was conceived as long ago as 1968, but the transferable fuel load for the initial version was only 10 tonnes, which was insufficient, so development was shelved. When the higher performance Il-76 became available the tanker project was restarted in 1982 as the Il-78.
Early versions of the Il-78 have the fuselage pod mounted on a short horizontal pylon, but the Il-78M has the fuselage pod suspended from an identical pylon to the wing pods, attached to a short stub wing. This modification was served to isolate the pod from turbulence generated by the fuselage, with the added benefit of commonality with the wing pod/pylon combination. Some Il-78s were produced with Aeroflot colours and civilian registrations, but production Il-78Ms received military markings, registration and colour scheme.
The majority of the twenty Il-78 aircraft of the Ukrainian Air Force have been permanently converted to pure transports, freight hold tanks and refuelling equipment being removed.
|
 |

| A Russian Airborne early warning and control A-50 is well represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
Another Russian Airborne early warning and control A-50 is well represented by Le Bras in the second episode of the story story LES OISEAUX NOIRS |

|
 |
The Beriev A-50 (NATO reporting name "Mainstay") is a Soviet-built Airborne early warning and control (AEW) aircraft based on the Ilyushin Il-76 transport. The existence of the A-50 was revealed in 1980 by Adolf Tolkachev.[1] Developed to replace the Tupolev Tu-126 "Moss", the A-50 first flew in 1978. It entered service in 1984, with about 40 produced by 1992.
The mission personnel of the 15-man crew derive data from the large Liana surveillance radar with its antenna in an over-fuselage rotodome, which has a diameter of 29 ft 9 in (9.00 m).
The A-50 can control up to 10 fighter aircraft for either air-to-air intercept or air-to-ground attack missions. The A-50 is capable of flying for 4 hours at 1000 km from its base at a maximum takeoff weight of 190 tons. The aircraft can be refuelled by Il-78 tankers.
The radar "Vega-M" is designed by MNIIP, Moscow, and produced by NPO Vega. The "Vega-M" is capable of tracking up to 50 targets simultaneously within 230 kilometers. Large targets, like surface ships, can be tracked at a distance of 400 km.
|

| A Russian navy Kamov Ka-27 is well represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
A Russian navy Kamov Ka-27 is also well represented by Formosa in the story OPERATION VEKTOR |

|
 |
The Kamov Ka-27 (NATO reporting name "Helix") is a military helicopter developed for the Soviet Navy, and currently in service in various countries including Russia, Ukraine, Vietnam, People's Republic of China, Republic of Korea (South Korea), and India. Variants include the Ka-29 assault transport, the Ka-28 downgraded export version, and the Ka-32 for civilian use.
The helicopter was developed for ferrying and anti-submarine warfare. Design work began in 1969 and the first prototype flew in 1973. It was intended to replace the decade-old Kamov Ka-25, and is similar in appearance to its predecessor due to the requirements of fitting in the same hangar space. Like other Kamov military helicopters it has coaxial rotors, removing the need for a tail rotor.
|
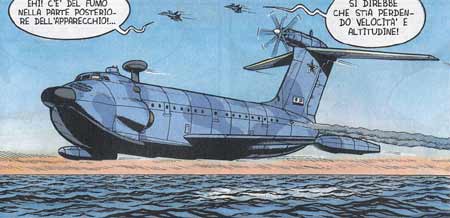
| The experimental Russian Navy ground effect vehicle A-90 Orlyonok (in the story named Orlan) is well represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE |
The A-90 Orlyonok (English: "Eaglet") is a Soviet ekranoplan (a ground effect vehicle) that was designed by Rostislav Evgenievich Alexeyev of the Central Hydrofoil Design Bureau.
The A-90 uses ground effect to fly a few meters above the surface. The Russians classify it as Ekranoplan Class B - it can achieve an altitude of 3,000 m (9,800 ft), placing between Class A - which is limited to ground effect, and Class C, which exploits the ground effect only during take-offs and landings.
The layout of the engines on the Orlyonok was unusual and a testament of the special needs of such an unconventional aircraft. Mounted in the top of the tail, it featured a massive Kuznetsov NK-12 turboprop, the most powerful turboprop ever made, which provided cruise power. The nose of the aircraft mounted two turbofan engines with the intakes on top of the nose and the exhaust along the side of the fuselage, the thrust of these engines being vectored under the wings to produce PAR thrust (increased lift and extra propulsion) for takeoff. Under cruise conditions and in ground effect, the front engines could be shut off since their power was unnecessary to keep the aircraft lifted, this also minimized intake of water, salt and ingestion of low flying birds.
Both takeoff and landing were assisted with large span-length flaps that greatly increased lift and could capture PAR thrust for increased air pressure. Water landings were assisted with a hydro-ski that extended out of the belly of the craft below the main wings.
The front end of the Orlyonok was hinged behind the radome and the whole assembly could open sideways to speed disembarkation of the infantry it carried, or of a BTR armoured personnel carrier. The Orlyonok had a built in folding ramp that allowed it to load and unload vehicles with no external support.
There were plans to resume production of the Orlyonok. The craft would be built in Petrozavodsk
) that was designed by Rostislav Evgenievich Alexeyev of the Central Hydrofoil Design Bureau.
The A-90 uses ground effect to fly a few meters above the surface. The Russians classify it as Ekranoplan Class B - it can achieve an altitude of 3,000 m (9,800 ft), placing between Class A - which is limited to ground effect, and Class C, which exploits the ground effect only during take-offs and landings.The Orlyonok was designed as a transport and also as a beach assault vehicle. Unlike other Soviet Ekranoplan designs, the Orlyonok was amphibious and was equipped with wheels for beaching and land based takeoffs.
|
 |
|
General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon
|

| Some F-16 used by "Unofficial Squadron" in Bosnia are shown by Bergese in the adventure L'ESCADRILLE FANTOME |
An USAF F-16 based on south Korea is represented by Bergese in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT. |

|

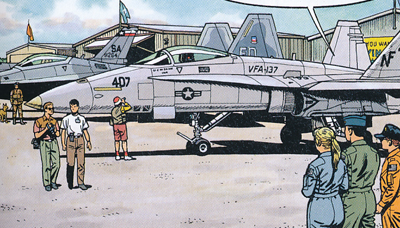
| The F-16 of the USAF aerobatic team Thunderbirds are well depicted by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
An Israelian Air Force F-16 is also represented by Winis in the story COBRA NOIR |

|
| A USAF unmanned and computer controlled F-16 of the Skyborg program is shown in the story PROGRAMME SKYBORG and AIR FORCE ONE |

| The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics (now Lockheed Martin) for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather multirole aircraft. Over 4,500 aircraft have been built since production was approved in 1976. Although no longer being purchased by the U.S. Air Force, improved versions are still being built for export customers. In 1993, General Dynamics sold its aircraft manufacturing business to the Lockheed Corporation, which in turn became part of Lockheed Martin after a 1995 merger with Martin Marietta.
The Fighting Falcon has key features including a frameless bubble canopy for better visibility, side-mounted control stick to ease control while maneuvering, a seat reclined 30 degrees to reduce the effect of g-forces on the pilot, and the first use of a relaxed static stability/fly-by-wire flight control system which helps to make it a nimble aircraft. The F-16 has an internal M61 Vulcan cannon and 11 locations for mounting weapons and other mission equipment. The F-16's official name is "Fighting Falcon", but "Viper" is commonly used by its pilots and crews, due to a perceived resemblance to a viper snake as well as the Battlestar Galactica Colonial Viper starfighter.
In addition to active duty U.S. Air Force, Air Force Reserve Command, and Air National Guard units, the aircraft is also used by the USAF aerial demonstration team, the U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds, and as an adversary/aggressor aircraft by the United States Navy. The F-16 has also been procured to serve in the air forces of 25 other nations. As of 2015, it is the second most common currently operational military aircraft in the world. |
|
McDonnell/Boeing F/A-18 Hornet and Super Hornet
|

| An early representation of a misterious F-18 piloted by Lady X is shown by Hubinon in the humoristic story MISSION IMPOSSIBLE published in the album 11 of TOUT BUCK DANNY. |
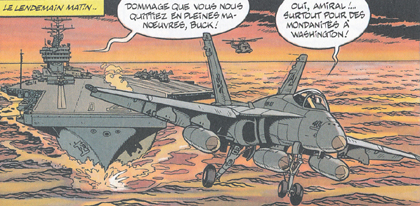
Buck Danny and his friends are flying on the F/A-18C well depicted by Bergese in the adventure LES AGRESSEUR. |
 |

| In the same story also a two seat F-18B is represented. |
Buck Danny is also flow on a F-18C in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE.
|
 |
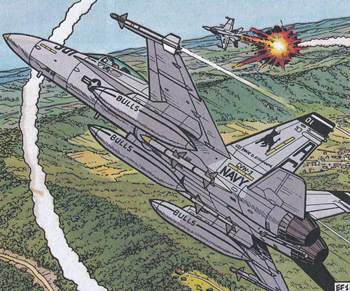 |
Buck Danny and friends are also flying the F-18C over Bosnia in the adventure L'ESCADRILLE FANTOME.
|
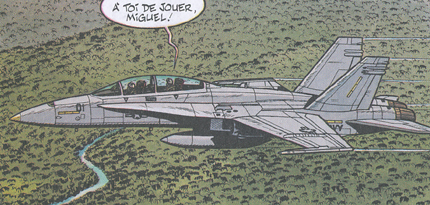
Buck Danny and friends are F-18 instructors for the fantasy state of Managua Air Force in the adventures ZONE INTERDITE and TONNERRE SUR LA CORDILLERE
|
 |
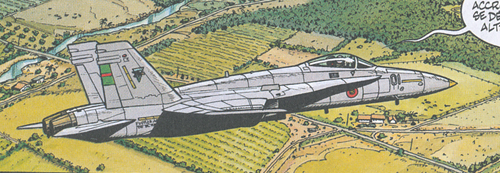 |
In the same adventures also an F-18C in the colur of the Managua Air Force is depicted by Bergese.
|
Cindy McPherson is flying an F-18C in the Air Show of the Bergese story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS
|
 |
 |
Our friends are still flying the F-18C Hornet in the story MYSTERE EN ANTARCTIQUE.
|
 |
An F-18C of the US Marines squadron VMFA-314 is also visible in the story PORTÈ DISPARU.
|
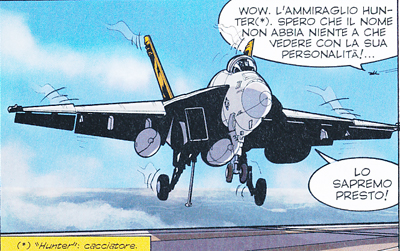
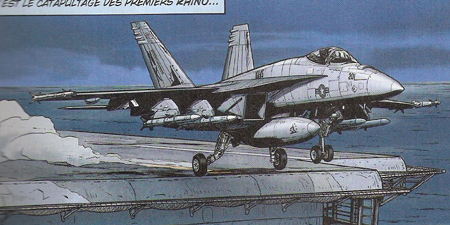
At the beggining of the story COBRA NOIR Buck Danny and friends are flying the new advanced version of the F-18, the F/A-18E Super Hornet.
|
 |
The F/A-18E Super Hornet are also present in the stories LA NUIT DU SPECTRE, DEFCON ONE and LE PACTE!
|
 |
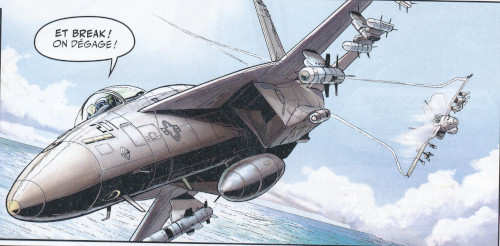 |
Some F/A-18E Super Hornet are represented by Philippe in the adventures TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE and ORBITE MORTELLE.
|
A beautiful The F/A-18F Super Hornet is also well represented in the story TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE
|
 |
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) F/A-18 Hornet is a twin-engine supersonic, all-weather carrier-capable multirole combat jet, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (F/A designation for Fighter/Attack). Designed by McDonnell Douglas and Northrop, the F/A-18 was derived from the latter's YF-17 in the 1970s for use by the United States Navy and Marine Corps. The Hornet is also used by the air forces of several other nations. The U.S. Navy's Flight Demonstration Squadron, the Blue Angels, has used the Hornet since 1986.
The F/A-18 has a top speed of Mach 1.8 (1,034 knots, 1,190 mph or 1,915 km/h at 40,000 ft or 12,190 m). It can carry a wide variety of bombs and missiles, including air-to-air and air-to-ground, supplemented by the 20 mm M61 Vulcan cannon. It is powered by two General Electric F404 turbofan engines, which give the aircraft a high thrust-to-weight ratio. The F/A-18 has excellent aerodynamic characteristics, primarily attributed to its leading edge extensions (LEX). The fighter's primary missions are fighter escort, fleet air defense, Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD), air interdiction, close air support and aerial reconnaissance. Its versatility and reliability have proven it to be a valuable carrier asset, though it has been criticized for its lack of range and payload compared to its earlier contemporaries, such as the Grumman F-14 Tomcat in the fighter and strike fighter role, and the Grumman A-6 Intruder and LTV A-7 Corsair II in the attack role.
The Hornet saw its first combat action in 1986 during the 1986 United States bombing of Libya and subsequently participated in 1991 Gulf War and 2003 Iraq War. The F/A-18 Hornet provided the baseline design for the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, a larger, evolutionary redesign of the F/A-18.
|
 |
 |
The Boeing F/A-18E Super Hornet and related twin-seat F/A-18F are twin-engine carrier-capable multirole fighter aircraft variants based on the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. The F/A-18E single-seat and F/A-18F tandem-seat variants are larger and more advanced derivatives of the F/A-18C and D Hornet. The Super Hornet has an internal 20 mm M61 rotary cannon and can carry air-to-air missiles and air-to-surface weapons. Additional fuel can be carried in up to five external fuel tanks and the aircraft can be configured as an airborne tanker by adding an external air refueling system.
Designed and initially produced by McDonnell Douglas, the Super Hornet first flew in 1995. Full-rate production began in September 1997, after the merger of McDonnell Douglas and Boeing the previous month. The Super Hornet entered service with the United States Navy in 1999, replacing the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, which was retired in 2006; the Super Hornet serves alongside the original Hornet. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), which has operated the F/A-18A as its main fighter since 1984, ordered the F/A-18F in 2007 to replace its aging F-111 fleet. RAAF Super Hornets entered service in December 2010.
|
|
Mikoyan-Gourevitch MIG-29 |
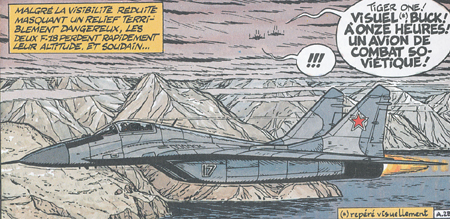 |
A Russian MIG-29 "Fulcrum A" is well depicted by Bergese in the story LES AGRESSEUR.
|
Some Russian MIG-29 are also shown in the story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE. |
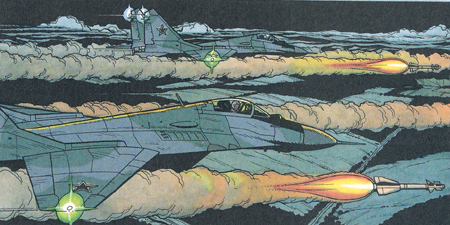 |
In the same story LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE also the naval version of the MIG-29 designated as MIG-29K is shown on board of the Russian aircraft carrier Admiral Kusnetzov. |
 |
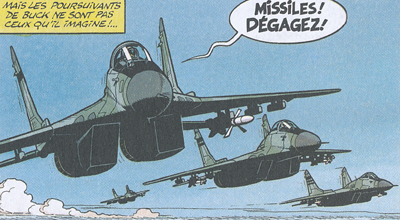 |
Some MIG-29 piloted by the mercenary pilots of Lady X organization are shown over Serbia in the story L'ESCADRILLE FANTOME |
A North Korean MIG-29 is well depicted by Bergese in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT
|  |
 |
Some MIG-29 of the fantasy state of Basran are shown in the adventure COBRA NOIR. |
 |
Some MIG-29K are also represented by Formosa in the adventure OPERATION VEKTOR. |
The Mikoyan MiG-29 (NATO reporting name: "Fulcrum") is a twin-engine jet fighter aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. Developed by the Mikoyan design bureau as an air superiority fighter during the 1970s, the MiG-29, along with the larger Sukhoi Su-27, was developed to counter new American fighters such as the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle, and the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon.The MiG-29 entered service with the Soviet Air Force in 1982.
While originally oriented towards combat against any enemy aircraft, many MiG-29s have been furnished as multirole fighters capable of performing a number of different operations, and are commonly outfitted to use a range of air-to-surface armaments and precision munitions. The MiG-29 has been manufactured in several major variants, including the multirole Mikoyan MiG-29M and the navalised Mikoyan MiG-29K; the most advanced member of the family to date is the Mikoyan MiG-35. Later models frequently feature improved engines, glass cockpits with HOTAS-compatible flight controls, modern radar and IRST sensors, and considerably increased fuel capacity; some aircraft have also been equipped for aerial refuelling.
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the militaries of a number of former Soviet republics have continued to operate the MiG-29, the largest of which is the Russian Air Force. The Russian Air Force wanted to upgrade its existing fleet to the modernised MiG-29SMT configuration, but financial difficulties have limited deliveries. The MiG-29 has also been a popular export aircraft; more than 30 nations either operate or have operated the aircraft to date, India being one of the largest export operators of the type. As of 2013, the MiG-29 is in production by Mikoyan, a subsidiary of United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) since 2006.
|
 |
 |
The Mikoyan MiG-29K (NATO reporting name: Fulcrum-D) is a Russian all-weather carrier-based multirole fighter aircraft developed by the Mikoyan design bureau. The MiG-29K was developed in the late 1980s from MiG-29M. Mikoyan describes it as a 4++ generation aircraft.
Production MiG-29Ks differ from prototypes by features such as a multi-function radar and several new cockpit displays; the adoption of HOTAS (hands-on-throttle-and-stick) controls; the integration of RVV-AE (Also known as R-77) air-to-air missiles, along with missiles for anti-ship and anti-radar operations; and several ground/strike precision-guided weapons.
The MiG-29K was not ordered into production and only two prototypes were originally built because the Russian Navy preferred the Su-27K in the early 1990s. The Mikoyan Design Bureau did not stop its work on the MiG-29K aircraft despite the lack of financing since 1992. The programme got a boost in the late 1990s to meet an Indian requirement for a ship-borne fighter following the purchase of a former Soviet aircraft carrier. It was first received by the Indian Naval Air Arm in 2009.
|
 |
Several North Korean Sukhoi Su-25 are shown by Bergese in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT.
|
The Sukhoi Su-25 Grach (NATO reporting name: "Frogfoot") is a single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by the Sukhoi Design Bureau. It was designed to provide close air support for the Soviet Ground Forces. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 22 February 1975. After testing, the aircraft went into series production in 1978 at Tbilisi in the Soviet Republic of Georgia.
Early variants included the Su-25UB two-seat trainer, the Su-25BM for target-towing, and the Su-25K for export customers. Some aircraft were being upgraded to Su-25SM standard in 2012. The Su-25T and the Su-25TM (also known as the Su-39) were further developments, not produced in significant numbers. The Su-25, and the Su-34, were the only armoured, fixed-wing aircraft in production in 2007. Su-25s are in service with Russia, other CIS states, and export customers.
The type has seen combat in several conflicts during its more than 30 years in service. It was heavily involved in the Soviet war in Afghanistan, flying counter-insurgency missions against the Mujahideen. The Iraqi Air Force employed Su-25s against Iran during the 1980–88 Iran–Iraq War. Most were later destroyed or flown to Iran in the 1991 Persian Gulf War. Abkhazian separatists used Su-25s during the Abkhazian War from 1992 to 1993. The Macedonian Air Force used Su-25s against Albanian insurgents in the 2001 Macedonia conflict and, in 2008, Georgia and Russia both used Su-25s in the Russo-Georgian War. African states, including the Ivory Coast, Chad, and Sudan have used the Su-25 in local insurgencies and civil wars. Recently the Su-25 has seen service in the Russian intervention in the Syrian Civil War.
|
 |
|
Boeing RC-135 Rivet Joint |
 |
A Boeing RC-135 Rivet Joint is represented by Bergese in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT.
|
The Boeing RC-135 is a family of large reconnaissance aircraft built by Boeing and modified by a number of companies, including General Dynamics, Lockheed, LTV, E-Systems, and L-3 Communications, and used by the United States Air Force and Royal Air Force to support theater and national level intelligence consumers with near real-time on-scene collection, analysis and dissemination capabilities. Based on the C-135 Stratolifter airframe, various types of RC-135s have been in service since 1961. Unlike the C-135 and KC-135 which are recognized by Boeing as the Model 717, the RC-135 is internally designated as the Model 739 by the company. Many variants have been modified numerous times, resulting in a large variety of designations, configurations, and program names.
|
 |
 |
A US Government Gulfstream IV seems represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The Gulfstream IV (or G-IV or GIV) and derivatives are a family of twinjet aircraft, mainly for private or business use. The aircraft was designed and built by Gulfstream Aerospace, a General Dynamics company based in Savannah, Georgia, United States from 1985 until 2003.
The U.S. military variant of the IV, designated C-20F/G/H/J Gulfstream IV in Department of Defense service. The C-20F is a GIV model operated by the U.S. Army in a command/executive transport role.
U.S. Marine Corps VIP C-20G, also known as the "Grey Ghost."
The C-20G aircraft may be configured for cargo operations, 26 passenger operations or combinations of the two. With passengers seats removed, it may be configured as three pallets with no passengers or two pallets and eight passengers or one pallet and fourteen passengers. With full seating, the aircraft is capable of accommodating up to twenty-six passengers and a crew of four. A hydraulically operated cargo door is installed on the starboard side of the aircraft, and a ball roller cargo floor is capable of accommodating palletized cargo. The C-20G is operated by Fleet Logistics Support Squadron Four Eight (VR-48) at Naval Air Facility, Andrews Air Force Base, Washington, DC and at VMR Detachment Kaneohe Bay, Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay, Marine Corps Base Hawaii.
|
 |
 |
Some French Navy Rafale M of the aircrfat carrier Charles de Gaule are well represented by Bergese in the story MYSTERE EN ANTARCTIQUE.
|
Some French Navy Rafale M of the aircrfat carrier Charles de Gaule are also well represented by Formosa in the story VOSTOK NE REPOND PLUS and OPERATION VEKTOR.
|  |
 |
The Dassault Rafale (literally meaning "gust of wind", and "burst of fire" in a more military sense) is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. Equipped with a wide range of weapons, the Rafale is intended to perform air supremacy, interdiction, aerial reconnaissance, ground support, in-depth strike, anti-ship strike and nuclear deterrence missions. The Rafale is referred to as an "omnirole" aircraft by Dassault.
In the late 1970s, the French Air Force and Navy were seeking to replace and consolidate their current fleets of aircraft. In order to reduce development costs and boost prospective sales, France entered into an arrangement with four other European nations to produce an agile multi-purpose fighter. Subsequent disagreements over workshare and differing requirements led to France's pursuit of its own development program. Dassault built a technology demonstrator which first flew in July 1986 as part of an eight-year flight-test programme, paving the way for the go-ahead of the project. The Rafale is distinct from other European fighters of its era in that it is almost entirely built by one country, involving most of France's major defence contractors, such as Dassault, Thales and Safran.
Many of the aircraft's avionics and features, such as direct voice input, the RBE2 AA active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar and the optronique secteur frontal infra-red search and track (IRST) sensor, were domestically developed and produced for the Rafale programme. Originally scheduled to enter service in 1996, the Rafale suffered significant delays due to post-Cold War budget cuts and changes in priorities. The aircraft is available in three main variants: Rafale C single-seat land-based version, Rafale B twin-seat land-based version, and Rafale M single-seat carrier-based version.
Introduced in 2001, the Rafale is being produced for both the French Air Force and for carrier-based operations in the French Navy. The Rafale has been marketed for export to several countries, and it has been selected for purchase by the Indian Air Force, the Egyptian Air Force, and the Qatar Air Force. The Rafale has been used in combat over Afghanistan, Libya, Mali, Iraq and Syria. Several upgrades to the weapons and avionics of the Rafale are planned to be introduced by 2018
|
 |
A French Navy AS 565 Panther of the aircrfat carrier Charles de Gaule is also represented by Bergese in the story MYSTERE EN ANTARCTIQUE.
|
| An AS 565 Panther is also well represented by Formosa in the story DEFCON ONE. |
 |
 |
The Eurocopter AS565 Panther is the military version of the Eurocopter AS365 Dauphin medium-weight multi-purpose twin-engine helicopter. The Panther is used for a wide range of military roles, including combat assault, fire support, anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, search and rescue, and medical evacuation (MEDEVAC).
During the 1980s, French aerospace firm Aerospatiale decided to develop a purpose-built military version of their popular Eurocopter AS365 Dauphin. The civil SA365 N variant of the Dauphin was used as the starting point for the project; the new rotorcraft was designed to perform utility, anti-tank, troop-transport, and maritime operations. On 28 February 1984, the military variant prototype, designated as the AS365M and later named Panther, conducted its first flight. A total of three prototypes were built.
In May 1986, Aerospatiale formally launched production of the AS365M, at which point the firm anticipated more than 400 Panthers to be sold in the long term. The initial production model, which was initially designated as the AS365 K, was shortly re-designated and became widely known as the AS565 Panther. Early models were powered by a pair of Turbomeca Arriel 1M1 turboshaft engines; in 1995, Eurocopter began offering higher powered versions of the Panther that used the new Turbomeca Arriel 2C engine instead.
In February 2016, Airbus Helicopters promised to relocate the global production line for the AS565 Panther to India if it is selected by the Indian Navy for a proposed utility helicopter acquisition.
|
An USAF C-21A is well represented by Bergese in the story PORTÈ DISPARU.
|  |
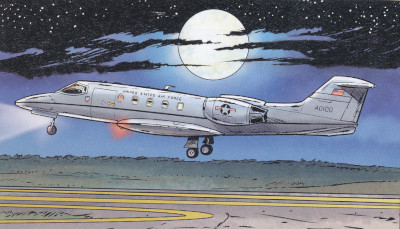 |
An USAF C-21A is also well represented by Formosa in the story AIR FORCE ONE.
|
The Learjet Model 35 and Model 36 are a series of American multi-role business jets and military transport aircraft manufactured by Learjet. When used by the United States Air Force they carry the designation C-21A.
The aircraft are powered by two Garrett TFE731-2 turbofan engines. Its cabin can be arranged for 6-8 passengers. The longer-range Model 36 has a shortened passenger area to provide more space in the aft fuselage for fuel tanks.
The engines are mounted in nacelles on the sides of the aft fuselage. The wings are equipped with single-slotted flaps. The wingtip fuel tanks distinguish the design from other aircraft having similar functions.
|
 |
|
McDonnell Douglas-BAe AV-8B Harrier II |
 |
Two AV-8B Harrier II of the US Marines are well depicted by Bergese in the story PORTÈ DISPARU.
|
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) AV-8B Harrier II is a single-engine ground-attack aircraft that constitutes the second generation of the Harrier Jump Jet family. Capable of vertical or short takeoff and landing (V/STOL), the aircraft was designed in the late 1970s as an Anglo-American development of the British Hawker Siddeley Harrier, the first operational V/STOL aircraft. Named after a bird of prey,[8] it is primarily employed on light attack or multi-role missions, ranging from close air support of ground troops to armed reconnaissance. The AV-8B is used by the United States Marine Corps (USMC), the Spanish Navy, and the Italian Navy. A variant of the AV-8B, the British Aerospace Harrier II, was developed for the British military, while another, the TAV-8B, is a dedicated two-seat trainer.
The project that eventually led to the AV-8B's creation started in the early 1970s as a cooperative effort between the United States and United Kingdom (UK), aimed at addressing the operational inadequacies of the first-generation Harrier. Early efforts centered on a larger, more powerful Pegasus engine to dramatically improve the capabilities of the Harrier. Due to budgetary constraints, the UK abandoned the project in 1975.
Following the withdrawal of the UK, McDonnell Douglas extensively redesigned the earlier AV-8A Harrier to create the AV-8B. While retaining the general layout of its predecessor, the aircraft incorporates a new wing, an elevated cockpit, a redesigned fuselage, one extra hardpoint per wing, and other structural and aerodynamic refinements. The aircraft is powered by an upgraded version of the Pegasus, which gives the aircraft its V/STOL ability. The AV-8B made its maiden flight in November 1981 and entered service with the USMC in January 1985. Later upgrades added a night-attack capability and radar, resulting in the AV-8B(NA) and AV-8B Harrier II Plus, respectively. An enlarged version named Harrier III was also studied, but not pursued. The UK, through British Aerospace, re-joined the improved Harrier project as a partner in 1981, giving it a significant work-share in the project. After corporate mergers in the 1990s, Boeing and BAE Systems have jointly supported the program. Approximately 340 aircraft were produced in a 22-year production program that ended in 2003.
|
 |
 |
Some French Air Force Mirage 2000 C over Bosnia are well shown by Bergese in the story L'ESCADRILLE FANTOME.
|
The Dassault Mirage 2000 is a French multirole, single-engine fourth-generation jet fighter manufactured by Dassault Aviation. It was designed in the late 1970s as a lightweight fighter based on the Mirage III for the French Air Force (Armée de l'Air). The Mirage 2000 evolved into a multirole aircraft with several variants developed, with sales to a number of nations. The variants include the Mirage 2000N and 2000D strike variants, the improved Mirage 2000-5 and several export variants. Over 600 aircraft were built and it has been in service with nine nations.
|
 |
 |
A Turboshaft-powered helicopter Robinson R66 is represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The Robinson R66 is a Turboshaft-powered helicopter designed and built by the Robinson Helicopter Company. It has five seats and a separate cargo compartment and is powered by a Rolls-Royce RR300 turboshaft. The R66 is slightly faster and smoother than the Robinson R44 from which it is derived. The R66 received both type and production certificates from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on October 25, 2010. Deliveries started in November 2010
|
 |
 |
Some Hot air balloon are also shown by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The hot air balloon is the first successful human-carrying flight technology. The first untethered manned hot air balloon flight was performed by Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier and François Laurent d'Arlandes on November 21, 1783, in Paris, France, in a balloon created by the Montgolfier brothers. The first hot-air balloon flown in the United States was launched from the Walnut Street Jail in Philadelphia on January 9, 1793 by the French aeronaut Jean Pierre Blanchard. Hot air balloons that can be propelled through the air rather than simply drifting with the wind are known as thermal airships.
A hot air balloon consists of a bag called the envelope that is capable of containing heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carries passengers and (usually) a source of heat, in most cases an open flame. The heated air inside the envelope makes it buoyant since it has a lower density than the relatively cold air outside the envelope. As with all aircraft, hot air balloons cannot fly beyond the atmosphere. Unlike gas balloons, the envelope does not have to be sealed at the bottom since the air near the bottom of the envelope is at the same pressure as the air surrounding. For modern sport balloons, the envelope is generally made from nylon fabric and the inlet of the balloon (closest to the burner flame) is made from fire resistant material such as Nomex. Beginning during the mid-1970s, balloon envelopes have been made in all kinds of shapes, such as rocket ships and the shapes of various commercial products, though the traditional shape remains popular for most non-commercial, and many commercial, applications.
|
 |
 |
Sonny Tuckson is flying a Powered paragliding in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
Powered paragliding, also known as paramotoring, is a form of ultralight aviation where the pilot wears a motor on his or her back (a paramotor) which provides enough thrust to take off using an adapted paraglider or paramotor wing. It can be launched in still air, and on level ground, by the pilot alone — no assistance is required.
In many countries, including the United States, powered paragliding is minimally regulated and requires no license. The ability to fly both low and slow safely, the 'open' feel, the minimal equipment and maintenance costs, and the portability are claimed to be this type of flying's greatest merits.
Powered paragliders usually fly between 15 and 50 mph (25 and 72 km/h) at altitudes from 'foot-dragging on the water' up to 24,000+ ft (5400 m) although most flying is done under 500 ft (150 m) AGL (above ground level). Due to the paramotor's slow forward speed, it must not be flown in conditions of high wind, turbulence, or intense thermal activity.
The paramotor, weighing from 45 to 90 pounds (20 to 40 kg) is supported by the pilot during takeoff. After a brief run (typically 10 feet or 3 metres) the wing lifts the motor and its harnessed pilot off the ground. After takeoff, the pilot gets into the seat and sits suspended beneath the inflated paraglider wing. Control is available using brake toggles for roll and a hand-held throttle for pitch.
Prices for a complete new package (wing, harness, and motor) vary from approximately 5,000 USD to 13,000 USD.
|
 |
|
Boeing C-17 Globemaster III |
 |
A Boeing C-17 Globemaster III is well represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The Boeing C-17 Globemaster III is a large military transport aircraft. It was developed for the United States Air Force (USAF) from the 1980s to the early 1990s by McDonnell Douglas. The C-17 carries forward the name of two previous piston-engined military cargo aircraft, the Douglas C-74 Globemaster and the Douglas C-124 Globemaster II. The C-17 commonly performs strategic airlift missions, transporting troops and cargo throughout the world; additional roles include tactical airlift, medical evacuation and airdrop duties. It was designed to replace the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter, and also fulfill some of the duties of the Lockheed C-5 Galaxy, freeing the C-5 fleet for outsize cargo.
Boeing, which merged with McDonnell Douglas in the 1990s, continued to manufacture C-17s for export customers following the end of deliveries to the U.S. Air Force. Aside from the United States, the C-17 is in service with the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, NATO Heavy Airlift Wing, India, and Kuwait. The final C-17 was completed at the Long Beach, California plant and flown on 29 November 2015.
|
 |
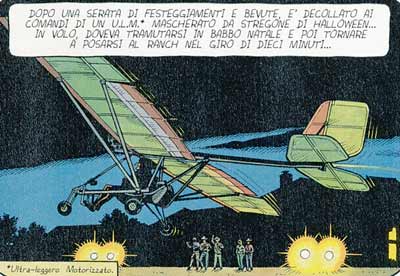 |
A ultralight aircraft Quicksilver MX is represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
 |
Another ultralight aircraft Quicksilver MX is also represented by Bergese in the story PROGRAMME SKYBORG.
|
Quicksilver is a line of single and two-place high wing, single-engine, ultralight aircraft that evolved from weight-shift hang gliders including Bob Lovejoy's High Tailer.
The earliest powered version, the Quicksilver C, was created as a self-launching hang glider, designed to allow pilots who lived in the flatlands to be able to self-launch without a hill. The design later evolved into an ultralight aircraft for powered cross-country flying.
The aircraft line has been in production since the late 1970s and remains in production in 2012 by Quicksilver Aircraft of Temecula, California
|
 |
 |
A ultralight aircraft Quicksilver GT 500 is also represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The Quicksilver GT500 is a family of strut-braced, high-wing, pusher configuration, tricycle gear aircraft built by Quicksilver Manufacturing of Temecula, California. The aircraft is available as a kit for amateur construction or as a completed ready-to-fly aircraft.
|
 |
 |
An aerobatic monoplane Extra EA-300 is represented by Bergese in the story SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
The Extra Flugzeugbau EA300 is a two-seat aerobatic monoplane capable of Unlimited category competition. It was designed in 1987 by Walter Extra, an award-winning German aerobatic pilot and built by Extra Flugzeugbau.
|
 |
 |
Two Royal Air Force Tornado F.3 (ADV) over Bosnia are well shown by Bergese in the story L'ESCADRILLE FANTOME.
|
Two Italian Air Force Tornado F.3 (ADV) over Afghanistan are also shown by Bergese in the story PORTÈ DISPARU.
|
 |
 |
The Panavia Tornado is a family of twin-engine, variable-sweep wing combat aircraft, which was jointly developed and manufactured by Italy, the United Kingdom, and West Germany. There are three primary Tornado variants: the Tornado IDS (interdictor/strike) fighter-bomber, the suppression of enemy air defences Tornado ECR (electronic combat/reconnaissance) and the Tornado ADV (air defence variant) interceptor aircraft.
The Tornado was developed and built by Panavia Aircraft GmbH, a tri-national consortium consisting of British Aerospace (previously British Aircraft Corporation), MBB of West Germany, and Aeritalia of Italy. It first flew on 14 August 1974 and was introduced into service in 1979–1980. Due to its multirole nature, it was able to replace several different fleets of aircraft in the adopting air forces. The Royal Saudi Air Force (RSAF) became the only export operator of the Tornado in addition to the three original partner nations. A tri-nation training and evaluation unit operating from RAF Cottesmore, the Tri-National Tornado Training Establishment, maintained a level of international co-operation beyond the production stage.
|
The Tornado was used by the Royal Air Force (RAF), Italian Air Force and RSAF during the 1991 Gulf War, in which the Tornado conducted many low-altitude penetrating strike missions. The Tornados of various operators were also used in conflicts in the former Yugoslavia during the Bosnian War and Kosovo War, the Iraq War, Libya during the Libyan civil war, as well as smaller roles in Afghanistan, Yemen, and Syria. Including all variants, 992 aircraft were built.
|
 |
 |
An USAF B-1B Lancer is well represented by Bergese in the adventure LES SECRETS DE LA MER NOIRE.
|
A decommissioned B-1B Lancer is represented by Formosa in the adventure LE PACTE!.
|  |
The Rockwell B-1 Lancer is a four-engine supersonic variable-sweep wing, jet-powered heavy strategic bomber used by the United States Air Force (USAF). It was first envisioned in the 1960s as a supersonic bomber with Mach 2 speed, and sufficient range and payload to replace the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress. It was developed into the B-1B, primarily a low-level penetrator with long range and Mach 1.25 speed capability at high altitude. It is commonly called the "Bone" (originally from "B-One").
Designed by Rockwell International (now part of Boeing), development was delayed multiple times over its history due to changes in the perceived need for manned bombers. The initial B-1A version was developed in the early 1970s, but its production was canceled, and only four prototypes were built. The need for a new platform once again surfaced in the early 1980s, and the aircraft resurfaced as the B-1B version with the focus on low-level penetration bombing. However, by this point, development of stealth technology was promising an aircraft of dramatically improved capability. Production went ahead as the B version would be operational before the "Advanced Technology Bomber" (which became the B-2 Spirit), during a period when the B-52 would be increasingly vulnerable. The B-1B entered service in 1986 with the USAF Strategic Air Command (SAC) as a nuclear bomber.
In the early 1990s, following the Gulf War and concurrent with the disestablishment of SAC and its reassignment to the newly formed Air Combat Command (ACC), the B-1B was converted to conventional bombing use. It first served in combat during Operation Desert Fox in 1998 and again during the NATO action in Kosovo the following year. The B-1B has supported U.S. and NATO military forces in Afghanistan and Iraq. The B-1B is expected to continue to serve into the 2030s, with the Long Range Strike Bomber to start supplementing the B-1B in 2030.
|
 |
 |
Some CV-22 Osprey of the USAF Special Operation Command are show by Winis in the story COBRA NOIR.
|
 |
Some V-22 Osprey of the US Marines are represented by Formosa in the story VOSTOK NE REPOND PLUS, OPERATION VEKTOR and LE PACTE!.
|
The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, tiltrotor military aircraft with both a vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL), and short takeoff and landing (STOL) capability. It is designed to combine the functionality of a conventional helicopter with the long-range, high-speed cruise performance of a turboprop aircraft.
The V-22 originated from the United States Department of Defense Joint-service Vertical take-off/landing Experimental (JVX) aircraft program started in 1981. The team of Bell Helicopter and Boeing Helicopters was awarded a development contract in 1983 for the tiltrotor aircraft. The Bell Boeing team jointly produce the aircraft. The V-22 first flew in 1989, and began flight testing and design alterations; the complexity and difficulties of being the first tiltrotor intended for military service in the world led to many years of development.
The United States Marine Corps began crew training for the Osprey in 2000, and fielded it in 2007; it supplemented and then replaced their Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knights. The Osprey's other operator, the U.S. Air Force, fielded their version of the tiltrotor in 2009. Since entering service with the U.S. Marine Corps and Air Force, the Osprey has been deployed in transportation and medivac operations over Iraq, Afghanistan, Libya and Kuwait.
|
 |
 |
A Spanish Army Eurocopter Tiger is alsoshow by Winis in the story COBRA NOIR.
|
The Airbus Helicopters Tiger, formerly known as the Eurocopter Tiger, is a four-bladed, twin-engined attack helicopter which first entered service in 2003. It is manufactured by Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters), the successor company to Aérospatiale's and DASA's respective helicopter divisions, which designate it as the EC665. In Germany it is known as the Tiger; in France and Spain it is called the Tigre.
Development of the Tiger started during the Cold War, and it was initially intended as an anti-tank helicopter platform to be used against a Soviet ground invasion of Western Europe. During its prolonged development period the Soviet Union collapsed, but France and Germany chose to proceed with the Tiger, developing it instead as a multirole attack helicopter. It achieved operational readiness in 2008.
The Tiger has the distinction of being the first all-composite helicopter developed in Europe; even the earliest models also incorporate other advanced features such as a glass cockpit, stealth technology, and high agility to increase its survivability. Improved variants have since entered service, outfitted with more powerful engines and compatible with a wider range of weapons. Since the type's introduction to service, Tigers have been used in combat in Afghanistan, Libya, and Mali.
|
 |
|
Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk and SH-60 Seahawk |
 |
The US Navy SH-60B Seahawk naval variant of the UH-60 Black Hawk is well represented by Bergese in the story LES SECRET DE LA MEIR NOIRE .
|
A UH-60 of the Custom and Border Protection Office of Air and Marine is show by Bergese at the beginning of the adventure ZONE INTERDITE. |
 |
 |
The SH-60F Seahawk is also well represented by Bergese in the story MYSTÈRE EN ANTARCTIQUE |
A UH-60 Black Hawk is also depicted by Bergese in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT
|  |
 |
A SH-60F Seahawk is also visible in the adventure by Zumbiehl and Winis COBRA NOIR. |
The SH-60F Seahawk is also depicted by Formosa in the stories LA NUIT DU SPECTRE, DEFCON ONE and LE PACTE!
|  |
 |
A H-60 Black Hawk is also depicted by Formosa in the adventure AIR FORCE ONE. |
The SH-60F Seahawk is also depicted by Philippe in the story TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE
|  |
 |
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-bladed, twin-engine, medium-lift utility helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky submitted the S-70 design for the United States Army's Utility Tactical Transport Aircraft System (UTTAS) competition in 1972. The Army designated the prototype as the YUH-60A and selected the Black Hawk as the winner of the program in 1976, after a fly-off competition with the Boeing Vertol YUH-61.
The UH-60A entered service with the U.S. Army in 1979, to replace the Bell UH-1 Iroquois as the Army's tactical transport helicopter. This was followed by the fielding of electronic warfare and special operations variants of the Black Hawk. Improved UH-60L and UH-60M utility variants have also been developed. Modified versions have also been developed for the U.S. Navy, Air Force, and Coast Guard. In addition to U.S. Army use, the UH-60 family has been exported to several nations. Black Hawks have served in combat during conflicts in Grenada, Panama, Iraq, Somalia, the Balkans, Afghanistan, and other areas in the Middle East.
|
The Sikorsky SH-60/MH-60 Seahawk (or Sea Hawk) is a twin turboshaft engine, multi-mission United States Navy helicopter based on the United States Army UH-60 Black Hawk and a member of the Sikorsky S-70 family. The most significant airframe modification is a hinged tail to reduce its footprint aboard ships.
The U.S. Navy uses the H-60 airframe under the model designations SH-60B, SH-60F, HH-60H, MH-60R, and MH-60S. Able to deploy aboard any air-capable frigate, destroyer, cruiser, fast combat support ship, amphibious assault ship, or aircraft carrier, the Seahawk can handle anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-surface warfare (ASUW), naval special warfare (NSW) insertion, search and rescue (SAR), combat search and rescue (CSAR), vertical replenishment (VERTREP), and medical evacuation (MEDEVAC). All Navy H-60s carry a rescue hoist for SAR/CSAR missions.
|  |
|
Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor |
 |
A Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor presented in the Fredericksburg (Texas) airshow is well depicted by Bergese in the adventure SABOTAGE AU TEXAS.
|
Some F-22 are also piloted by Buck Danny and his friends in the story LA NUIT DU SERPENT. |
 |
 |
An F-22 is shooting down near the Turkmenistan at the beginning of the story COBRA NOIR by Zumbiehl and Winis |
Buck Danny is also flying the F-22 Raptor in the adventure by Zumbiehl and Formosa LA NUIT DU SPECTRE
|  |
 |
Buck Danny and friends are also flying the F-22 Raptor in the adventure by Zumbiehl and Formosa PROGRAMME SKYBORG
|
Some F-22 Raptor excorting the Air Force One are shown by Formosa in the story AIR FORCE ONE
|  |
 |
Some F-22 Raptor are also shown in the adventure by Zumbiehl and Philippe TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE
|
The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor is a fifth-generation single-seat, twin-engine, all-weather stealth tactical fighter aircraft developed for the United States Air Force (USAF). The result of the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter program, the aircraft was designed primarily as an air superiority fighter, but has additional capabilities including ground attack, electronic warfare, and signals intelligence roles. Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor and was responsible for the majority of the airframe, weapon systems, and final assembly of the F-22, while program partner Boeing provided the wings, aft fuselage, avionics integration, and training systems.
The aircraft was variously designated F-22 and F/A-22 prior to formally entering service in December 2005 as the F-22A. After a protracted development and despite operational issues, the USAF considers the F-22 a critical component of its tactical air power, and states that the aircraft is unmatched by any known or projected fighter. The Raptor's combination of stealth, aerodynamic performance, and situational awareness gives the aircraft unprecedented air combat capabilities.
The high cost of the aircraft, a lack of clear air-to-air missions due to delays in Russian and Chinese fighter programs, a ban on exports, and development of the more versatile and comparatively lower cost F-35 led to the end of F-22 production. A final procurement tally of 187 operational production aircraft was established in 2009 and the last F-22 was delivered to the USAF in 2012.
. |
 |
 |
A Kawasaki P-1 Japanese maritime patrol aircraft is well represented by Formosa inthe adventure LA NUIT DU SPECTRE.
|
The Kawasaki P-1 (previously P-X, XP-1) is a Japanese maritime patrol aircraft in service with the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force as a replacement for the P-3C Orion. The JMSDF took delivery of the first two operational P-1 aircraft on 26 March 2013.
With its P-3C aircraft having been in service for twenty years, the JMSDF began to look for a replacement maritime patrol aircraft. Lockheed and the United States had been working on the Lockheed P-7 to replace its own P-3s, but the program had been cancelled. Since other similar aircraft (such as the Nimrod) did not meet the JMSDF's requirements, they decided to develop their own aircraft.
The project was intended to share many design components with the Kawasaki C-2, another local design intended to replace the C-1 and C-130H cargo aircraft. However, due to the very different roles of the two aircraft, only minimal similarities have been achieved. The merit rather lies in the sharing of development resources, allowing a large reduction in development costs.
|
 |
 |
A fantasy stealth advanced fighter TX-60 Spectre developed by Yamasaki corporation which works for a japanese criminal organization is show by Formosa in the stories LA NUIT DU SPECTRE and DEFCON ONE.
This advanced aircraft piloted in the story by Lady X is based on the Chinese fifth generation fighter Chengdu J-20
|
The Chengdu J-20 is a stealth, twinjet, fifth-generation fighter aircraft prototype being developed by China's Chengdu Aerospace Corporation for the Air Force (PLAAF). The J-20 made its first flight on 11 January 2011, and is expected to be operational in 2018.
China's J-20 platform has the potential to be a capable, long-range strike system in the Asia-Pacific region, with low rate initial production appearing to have begun as of January 2016.
The main weapon bay is capable of housing both short and long-range air-to-air missiles (AAM) (PL-9, PL-12C/D & PL-21).
Two smaller lateral weapon bays behind the air inlets are intended for short-range AAMs (PL-9). These bays allow closure of the bay doors prior to firing the missile, thus enhancing stealth.
|
 |
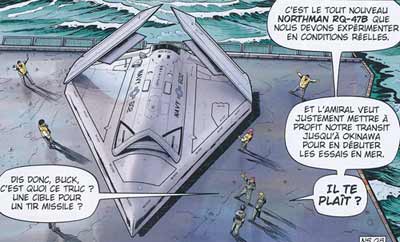 |
the unmanned combat air vehicle Northrop Grumman X-47B is shown on board of the USS Ronald Reagan in the story LA NUIT DU SPECTRE. In this adventure the veichicle is identified with the fantasy nomenclature of Northman RQ-47B and Sonny Tuckson was also in charge to remotelly fly it.
|
The Northrop Grumman X-47B is a demonstration unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) designed for aircraft carrier-based operations. Developed by the American defense technology company Northrop Grumman, the X-47 project began as part of DARPA's J-UCAS program, and subsequently became part of the United States Navy's Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration (UCAS-D) program. The X-47B is a tailless jet-powered blended-wing-body aircraft capable of semi-autonomous operation and aerial refuelling.
The X-47B first flew in 2011, and as of 2015, its two active demonstrators have undergone extensive flight and operational integration testing, having successfully performed a series of land- and carrier-based demonstrations. In August 2014, the US Navy announced that it had integrated the X-47B into carrier operations alongside manned aircraft,[6] and by May 2015 the aircraft's primary test program was declared complete. Northrop Grumman intends to develop the prototype X-47B into a battlefield-ready aircraft, the Unmanned Carrier-Launched Airborne Surveillance and Strike (UCLASS) system, which will enter service in the 2020s. The X-47B demonstrators themselves were intended to become museum exhibits after the completion of their flight testing, but the Navy later decided to maintain them in flying condition pending further development.
|
 |
 |
A Mitsubishi F-2 of the Japanese Air Force is well depicted by Formosa in the story LA NUIT DU SPECTRE
|
The Mitsubishi F-2 is a multirole fighter manufactured by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and Lockheed Martin for the Japan Air Self-Defense Force, with a 60/40 split in manufacturing between Japan and the USA. Production started in 1996 and the first aircraft entered service in 2000. The first 76 aircraft entered service in 2008, with a total of 94 airframes under contract.The first AESA Active electronically scanned array radar on a combat aircraft was the J/APG-1 introduced on the Mitsubishi F-2 in 1995. In 2005, the Ministry of Defense (Japan) changed the category from Support Fighter to Fighter.
The F-2 program was controversial, because the unit cost, which includes development costs, is roughly four times that of a Block 50/52 F-16, which does not include development costs. Inclusion of development costs distorts the incremental unit cost (this happens with most modern military aircraft), though even at the planned procurement levels, the price per aircraft was somewhat high. The initial plan of 141 F-2s would have reduced the unit cost by up to US$10 million(€7,5 million) per unit, not including reduced cost from mass production. As of 2008, 94 aircraft were planned. Also controversial is the amounts claimed to be paid to American side as various licensing fees, although making use of the pre-existing technology was much cheaper than trying to develop it from scratch.
|
 |
 |
In the story LA NUIT DU SPECTRE, Buck Danny is rescued by a flying boat ShinMaywa US-2 of the Japan Maritime Self Defense Force. |
The ShinMaywa (formerly Shin Meiwa) US-2 is a Japanese large STOL amphibious aircraft designed for air-sea rescue (SAR) work. The US-2 is scheduled to replace the older ShinMaywa US-1A.
The aircraft is currently operated by the 31st Fleet Air Wing (71st Air Force, 71st Flight Squadron) at Iwakuni air base and Atsugi air base.
|
 |
 |
Some Chinese Navy Shenyang J-15 from the aircraft carrier Liaoning are shown by Formosa in the stories LA NUIT DU SPECTRE and DEFCON ONE. |
The Shenyang J-15, also known as Flying Shark, is a carrier-based fighter aircraft in development by the Shenyang Aircraft Corporation and the 601 Institute for the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy's aircraft carriers. Rumors initially claimed the aircraft was to be a semi-stealth variant, yet later reports indicate the aircraft is based on the Soviet-designed Sukhoi Su-33 and is fitted with domestically produced radars, engines, and weapons. An unfinished Su-33 prototype, the T-10K-3, was acquired from Ukraine in 2001 and is said to have been studied extensively, with development on the J-15 beginning immediately afterward. While the J-15 appears to be structurally based on the Su-33, the indigenous fighter features Chinese technologies as well as avionics from the J-11B program.
|
 |
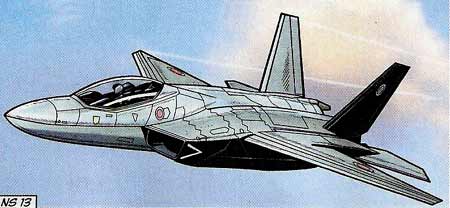 |
The Japanese prototype Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin is show by Formosa in the story LA NUIT DU SPECTRE.
In the reality this prototype was not yet ready for flight test in the late 2015. |
The Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin (formerly the ATD-X ) is a Japanese experimental aircraft for testing advanced stealth fighter aircraft technologies. It is being developed by the Japanese Ministry of Defense Technical Research and Development Institute (TRDI) for research purposes. The main contractor of the project is Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. Many consider this aircraft to be Japan's first domestically made stealth fighter. ATD-X is an acronym meaning "Advanced Technology Demonstrator – X". The aircraft is widely known in Japan as Shinshin (spirit of the heart) although the name itself is only an early codename within the Japan Self-Defense Forces; The name is not officially in use. The aircraft's first flight is scheduled for early in 2016.
|
 |
 |
The Chinese Navy helicopter Changhe Z-8J is well represented by Formosa in the story DEFCON ONE |
The Changhe Z-8 (Zhishengji-8) is a triple engine, multi-role helicopter designed and manufactured by the Changhe Aircraft Industry Group (CAIG) of China. It is derived from SA 321 Super Frelon Helicopter built by Aerospatiale.
The helicopter entered service in 1989. About 15 to 20 Z-8 helicopters are currently serving the People's Liberation Army Naval Air Force (PLANAF).
The Z-8 is fitted with a HS-12 dipping sonar, sonobuoys and an A244S torpedo under the fuselage section. It is also equipped with YJ-81 or YJ-83K air-to-surface missiles (ASM) for anti-ship operations.
|
 |
|
Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II |
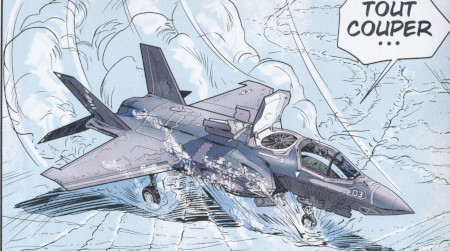 |
Three F-35B STOVL of US Marines are tested on board of USS Ronald Reagan in the South Pole cold environment by Buck Danny and his friends in the story VOSTOK NE REPOND PLUS, OPERATION VEKTOR and LE PACTE! |
 |
Some Australian Air Force F-35A are shown in the adventure TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE |
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a family of single-seat, single-engined, all-weather stealth multirole fighters. The fifth-generation combat aircraft is designed to perform ground-attack and air-superiority missions. It has three main models: the F-35A conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) variant, the F-35B short take-off and vertical-landing (STOVL) variant, and the F-35C carrier-based catapult-assisted take-off but arrested recovery (CATOBAR) variant.
The United States principally funds the F-35 JSF development, with additional funding from partners. The partner nations are either NATO members or close U.S. allies. The United Kingdom, Italy, Australia, Canada, Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Turkey are part of the active development program; several additional countries have ordered, or are considering ordering, the F-35.
The F-35A is the conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) variant intended for the U.S. Air Force and other air forces. It is the smallest, lightest F-35 version and is the only variant equipped with an internal cannon, the GAU-22/A. This 25 mm cannon is a development of the GAU-12 carried by the USMC's AV-8B Harrier II. It is designed for increased effectiveness against ground targets compared to the 20 mm M61 Vulcan cannon carried by other USAF fighters.
|
 |
 |
The F-35B is the short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) variant of the aircraft. Similar in size to the A variant, the B sacrifices about a third of the A variant's fuel volume to accommodate the vertical flight system. Vertical takeoffs and landings are riskier because of threats such as foreign object damage. Whereas the F-35A is stressed to 9 g, the F-35B's stress goal is 7 g. The first test flight of the F-35B was conducted on 11 June 2008. Another milestone, the first successful ski-jump launch was carried out by BAE test pilot Peter Wilson on 24 June 2015.
Unlike other variants, the F-35B has no landing hook. The "STOVL/HOOK" control instead engages conversion between normal and vertical flight. Jet thrust is sent directly downwards during vertical flight. The variant's three-bearing swivel nozzle that directs the full thrust of the engine is moved by a "fueldraulic" actuator using pressurized fuel as the working fluid
|
Compared to the F-35A, the F-35C carrier variant features larger wings with foldable wingtip sections, larger wing and tail control surfaces for improved low-speed control, stronger landing gear for the stresses of carrier arrested landings, a twin-wheel nose gear, and a stronger tailhook for use with carrier arrestor cables. The larger wing area allows for decreased landing speed while increasing both range and payload.
The United States Navy intends to buy 260 F-35Cs to replace the F/A-18A, B, C, and D Hornets and complement the Super Hornet fleet. On 27 June 2007, the F-35C completed its Air System Critical Design Review (CDR), allowing the production of the first two functional prototypes. The United States Marine Corps will also purchase 80 F-35Cs, enough for five squadrons, for use with navy carrier air wings in a joint service agreement signed on 14 March 2011. A recent 2014 document stated that the USMC will also have 4 squadrons of F-35Cs with 10 aircraft per squadron for the Marine Corps' contribution to U.S. Navy carrier air wings
|
 |
 |
The Lady X criminal group is using a Gulfstream G650 in the adventure OPERATION VEKTOR |
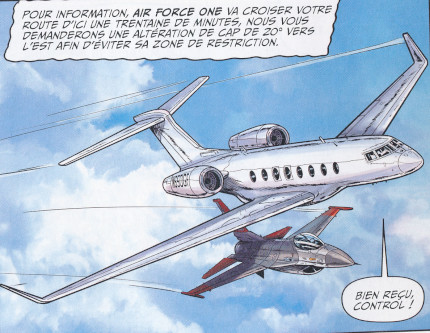 |
A Gulfstream G650 is also shown by Formosa in the adventure PROGRAMME SKYBORG and AIR FORCE ONE |
The Gulfstream G650 is a twin-engine business jet airplane produced by Gulfstream Aerospace. The model is designated Gulfstream GVI in its type certificate, and may be configured to carry from 11 to 18 passengers. Gulfstream began the G650 program in 2005 and revealed it to the public in 2008. The G650 is the company's largest and fastest business jet with a top speed of Mach 0.925.
The aircraft project was named the 2014 winner of the Collier Trophy, for having "strengthened business aviation through significant technological advancements in aircraft performance, cabin comfort, and safety." The G650ER is an extended-range version of the G650. The 300th was delivered in April 2018, just over five years since introduction in December 2012.
|
 |
 |
The helicopter NH-90 of the French Navy is represented by Formosa in the adventure OPERATION VEKTOR and LE PACTE ! |
The NHIndustries NH90 is a medium-sized, twin-engine, multi-role military helicopter. It was developed in response to NATO requirements for a battlefield helicopter which would also be capable of being operated in naval environments. The NH90 was developed and is manufactured by NHIndustries, a collaborative company, which is owned by Airbus Helicopters, Leonardo (formerly AgustaWestland) and Fokker Aerostructures. The first prototype conducted its maiden flight in December 1995; the type first entered operational service in 2007. As of July 2019, the NH90 has logged 185,000 flight hours in the armed forces of thirteen nations.
The NH90 has the distinction of being the first production helicopter to feature entirely fly by wire flight controls. There are two main variants, the Tactical Transport Helicopter (TTH) for army use and the navalised NATO Frigate Helicopter (NFH); each customer typically has various alterations and customisations made to their own NH90 fleets, such as different weapons, sensors and cabin arrangements, to meet their own specific requirements. In early service, the NH90 has suffered several teething issues, which has in turn delayed active deployment of the type by some operators.
|
 |
|
General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper |
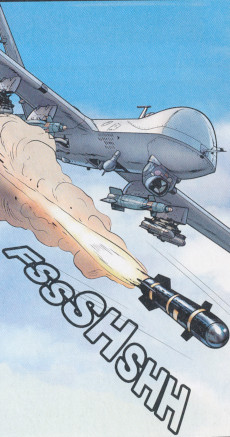 |
An unmanned aerial vehicle MQ-9 Reaper is shown by Formosa in the story LE PACTE ! |
The General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper (sometimes called Predator B) is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) capable of remotely controlled or autonomous flight operations developed by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) primarily for the United States Air Force (USAF). The MQ-9 and other UAVs are referred to as Remotely Piloted Vehicles/Aircraft (RPV/RPA) by the USAF to indicate their human ground controllers.
The MQ-9 is the first hunter-killer UAV designed for long-endurance, high-altitude surveillance. In 2006, the then–Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force General T. Michael Moseley said: "We've moved from using UAVs primarily in intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance roles before Operation Iraqi Freedom, to a true hunter-killer role with the Reaper."
The MQ-9 is a larger, heavier, and more capable aircraft than the earlier General Atomics MQ-1 Predator; it can be controlled by the same ground systems used to control MQ-1s. The Reaper has a 950-shaft-horsepower (712 kW) turboprop engine (compared to the Predator's 115 hp (86 kW) piston engine). The greater power allows the Reaper to carry 15 times more ordnance payload and cruise at about three times the speed of the MQ-1. The aircraft is monitored and controlled by aircrew in the Ground Control Station (GCS), including weapons employment.
|
 |
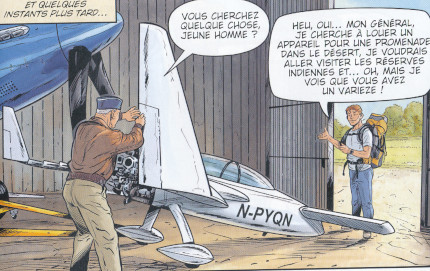 |
A composite canard home built aircraft belong to General Chuck Yeager is shown in the story PROGRAMME SKYBORG |
The Rutan VariEze is a composite, canard aircraft designed by Burt Rutan. It is a high-performance homebuilt aircraft, hundreds of which have been constructed. The design later evolved into the Long-EZ and other, larger cabin canard aircraft. The VariEze is notable for popularizing the canard configuration and moldless glass cloth composite construction for homebuilt aircraft.
|
 |
 |
The Eurocopter EC145 is used by the mercenary group of Sato in the story PROGRAMME SKYBORG and AIR FORCE ONE |
The Eurocopter EC145 (now Airbus Helicopters H145) is a twin-engine light utility helicopter developed and manufactured by Airbus Helicopters. Originally designated as the BK 117, the H145 is based upon the MBB/Kawasaki BK 117 C1, which became a part of the combined Eurocopter line-up in 1992 with the merger of Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm's helicopter division of Daimler-Benz into Eurocopter. The helicopter was earlier named EC145; an updated version, EC145 T2, was renamed H145 in 2015.
The H145 is a twin-engine aircraft and can carry up to nine passengers along with two crew, depending on customer configuration. The helicopter is marketed for passenger transport, corporate transport, emergency medical services (EMS), search and rescue, parapublic and utility roles.
Military variants of the helicopter have also been produced under various designations, such as H145M or UH-72, and have been used for training, logistics, medical evacuation, reconnaissance, light attack, and troop-transport operations.
|
 |
 |
A Boeing 777 of Airfrance is depicted by Formosa in the story PROGRAMME SKYBORG |
The Boeing 777, commonly referred to as the Triple Seven, is an American long-range wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. It is the world's largest twinjet. The 777 was designed to bridge the gap between Boeing's other wide body airplanes, the twin-engined 767 and quad-engined 747, and to replace older DC-10s and L-1011 trijets. Developed in consultation with eight major airlines, with a first meeting in January 1990, the program was launched on October 14, 1990, with an order from United Airlines. The prototype was rolled out on April 9, 1994, and first flew on June 12, 1994. The 777 entered service with the launch customer, United Airlines, on June 7, 1995. Longer range variants were launched on February 29, 2000, and were first delivered on April 29, 2004.
|
 |
 |
An helicopter Airbus H145 used by an international criminal organization is represented in the story TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE |
The Airbus Helicopters H145, formerly the Eurocopter EC145, is a twin-engine light utility helicopter developed and manufactured by Airbus Helicopters. Originally designated as the BK 117, the H145 is based upon the MBB/Kawasaki BK 117 C1, which became a part of the combined Eurocopter line-up in 1992 with the merger of Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm's helicopter division of Daimler-Benz into Eurocopter. The helicopter was initially named EC145; an updated version, EC145 T2, was renamed H145 in 2015. The helicopter was significantly updated in the 2020s with first a fenestron replacing the traditional tail rotor, followed later by a 5-blade main rotor head.
|
 |
|
NROL-25 (USA-234) Reconnaissance Satellite |
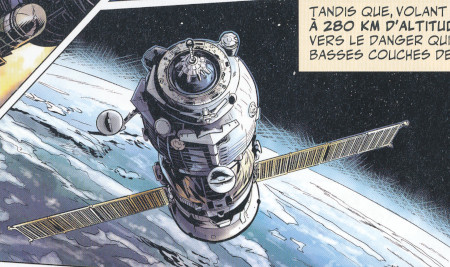 |
A fantasy representation of a Reconnaissance Satellite NROL-25 (USA-234) is shown in the story TRAQUE EN HAUTE ALTITUDE |
USA-234, also known as NRO Launch 25 or NROL-25, is an American reconnaissance satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in 2012, it has been identified as the second radar imaging satellite to be launched as part of the Future Imagery Architecture programme.
The satellite's orbit and mission are officially classified; however, it has been located by amateur observers in a 1,096 by 1,079 kilometres (681 by 670 mi) orbit, inclined at 123 degrees.
|
 |
| |